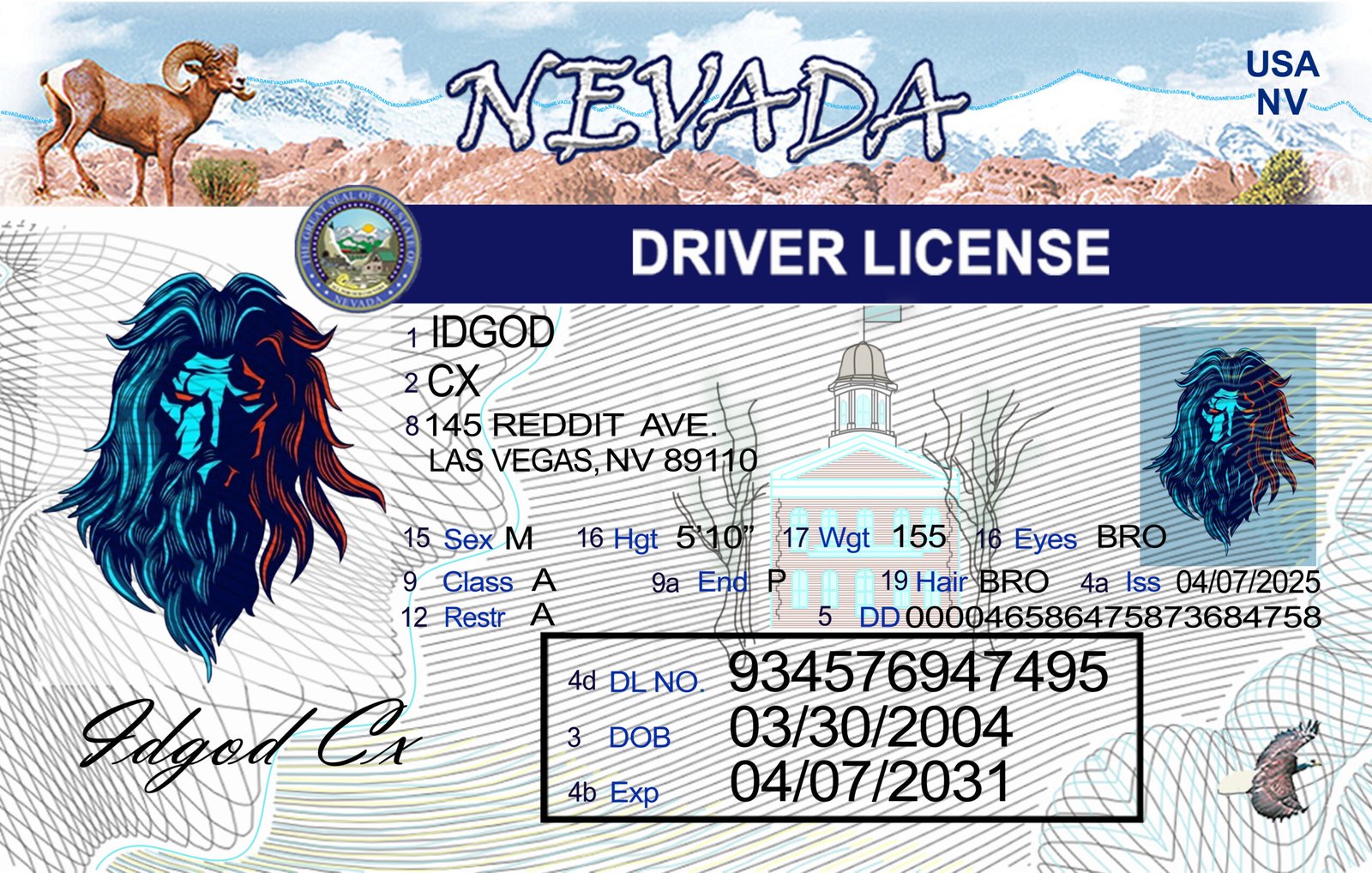
The Nevada driver’s license, issued by the Nevada Department of Motor Vehicles (ND DMV), is one of the most technologically advanced identification credentials in the western United States. Built for durability, authenticity, and robust identity protection, the modern Nevada driver’s license plays an essential role across industries and public institutions. From the casinos and entertainment venues along the Las Vegas Strip to government offices, banks, hospitals, and airports statewide, the Nevada license is used daily as an authoritative form of identity verification. Because the state has long navigated issues related to tourism, transient populations, and high-risk fraud environments, Nevada has become especially vigilant in building a licensing system fortified with advanced security systems and tamper-resistant features.
Nevada’s adoption of REAL ID served as a turning point, prompting a redesigned card architecture with improved materials, enhanced card printing methods, biometric verification protocols, and strict identity-proofing requirements. The license now incorporates powerful anti-counterfeit defenses, including polycarbonate construction, laser engraving, holographic imagery, UV-layered patterns, microprinting, and encrypted machine-readable zones. Together, these features help ensure that every credential issued is legitimate, durable, and extremely difficult to duplicate.
Types of Nevada Driver’s Licenses
Nevada offers several types of licenses and identification cards, all produced with the same high-security card technology:
Standard Driver’s License (Non-REAL ID)
Valid for everyday identification and driving but not accepted for certain federal purposes after REAL ID enforcement.REAL ID-Compliant License
Marked with a gold star, this credential is accepted for domestic flights, federal buildings, and secure federal facilities.Commercial Driver’s License (CDL)
Required for commercial vehicle operation and tied into federal identity-monitoring databases.ID Cards & Under-21 IDs
Non-driver identification using the same secure construction as driver’s licenses.Instruction Permits, Motorcycle Licenses, & Endorsements
Issued within Nevada’s secure digital licensing system and built using the same materials and protections.
All versions adhere to federal and state security guidelines designed to prevent fraudulent issuance.
Physical Security Features of the Nevada Driver’s License
The Nevada driver’s license incorporates multiple layers of physical security protections. Many are visible to the naked eye, while others are hidden or detectable only with specialized equipment. This layered approach ensures that counterfeiting, tampering, and replication remain extremely difficult.
1. Polycarbonate Card Material
Modern Nevada licenses are built from polycarbonate, one of the strongest and most secure ID materials available. Polycarbonate consists of fused layers, forming a single solid structure that:
Cannot be peeled or separated
Resists surface tampering, chemical alteration, and heat manipulation
Supports advanced laser engraving
Offers superior durability for long-term use
Because the material reacts visibly to tampering, any fraudulent attempt leaves clear signs of damage.
2. Laser-Engraved Text and Portrait
Nevada laser-engraves the cardholder’s personal data directly into the card body, including:
Full name
Date of birth
Address
License number
Signature
Portrait photo (rendered in grayscale)
Laser engraving embeds information below the surface rather than printing it on top, making alterations essentially impossible without destroying the card.
3. Multiple Portrait Images
To prevent photo substitution, the Nevada license displays the cardholder’s likeness in multiple formats:
A main portrait
A smaller ghost image positioned elsewhere
Subtle embedded facial markers in certain versions
These redundant images force counterfeiters to alter multiple card elements simultaneously—a task even advanced forgery operations cannot achieve cleanly.
4. UV-Specific Security Patterns
Like many high-security IDs, Nevada incorporates UV (ultraviolet) imagery into its card design. When placed under UV light, hidden features appear, such as:
State-specific symbols
Fluorescent shapes
Micro-UV text
Covert design layers not visible in normal lighting
These elements serve as a powerful verification system for law enforcement and identity screeners.
5. Holographic & Optically Variable Ink Features
The Nevada license includes holographic and optically variable elements that shift in color or brightness when the card is tilted. These include:
Embedded holographic overlays
Multitone reflective features
State-themed symbols with color-shifting ink
Because these elements require specialized manufacturing equipment, they are difficult for counterfeiters to replicate.
6. Fine-Line Guilloche Prints & Microprinting
Nevada incorporates detailed fine-line artwork—called guilloche patterns—into the card background. These intricate designs distort when copied, making counterfeit reproduction impractical.
Microprinting adds another layer of security through miniature text that:
Appears as a solid line to the naked eye
Becomes readable only under magnification
Blurs or pixelates when replicated by home printers or scanners
7. Laser-Perforated Features
Some Nevada licenses include laser-perforated symbols or numbers visible when held to a backlight. These micro-holes can be formed only with high-precision equipment, providing a strong anti-forgery barrier.
8. Tactile Elements
Portions of the license incorporate raised textures, such as numbers or symbols. These tactile features:
Allow quick authentication by touch
Aid visually impaired users
Provide an additional deterrent against fake IDs
Digital and Backend Security Components
Nevada pairs its physical card protections with advanced digital systems designed to secure the identity-verification process from the moment a person applies for a license.
1. Encrypted 2D Barcode (Machine-Readable Zone)
On the back of the Nevada license is a high-density, encrypted 2D barcode storing personal data. Scanners verify that this encoded information matches the printed information. Any mismatch suggests possible alteration or duplication.
2. REAL ID Document Requirements
REAL ID standards require strict documentation, including:
Proof of identity (passport, birth certificate, etc.)
Proof of Social Security number
Two documents proving Nevada residency
Lawful presence verification
These documents are electronically validated using secure national databases.
3. Biometric Facial Recognition
Nevada uses biometric facial recognition to check new applicant photos against existing images stored in the state database. This prevents:
Duplicate licenses
Alias identities
Reissuance after suspension or revocation
Identity theft attempts
Suspicious matches trigger a manual review by fraud specialists.
4. Centralized Production & Secure Card Issuance
All Nevada driver’s licenses are created in a secure centralized facility. This system:
Limits unauthorized access to blank card stock
Ensures consistent quality control
Reduces vulnerability to insider fraud
Allows secure tracking of production materials
5. CDL Federal Integration
Commercial license holders undergo additional security screening through:
CDLIS (Commercial Driver’s License Information System)
TSA background checks for HAZMAT endorsements
FMCSA national safety databases
This helps maintain identity integrity in interstate commercial driving.
Why Nevada’s Security Systems Matter
Nevada’s advanced licensing protections are essential for public safety, tourism security, and crime prevention. The state’s layered approach benefits residents by:
Preventing counterfeit ID circulation
Reducing identity theft and financial fraud
Strengthening airport and federal facility security through REAL ID
Supporting accurate law enforcement identification
Protecting minors from underage ID fraud
Ensuring trust in government-issued credentials
Because Nevada faces unique exposure to identity fraud risks due to its tourism and gaming industries, the state maintains some of the most robust and modern licensing protections in the western region.